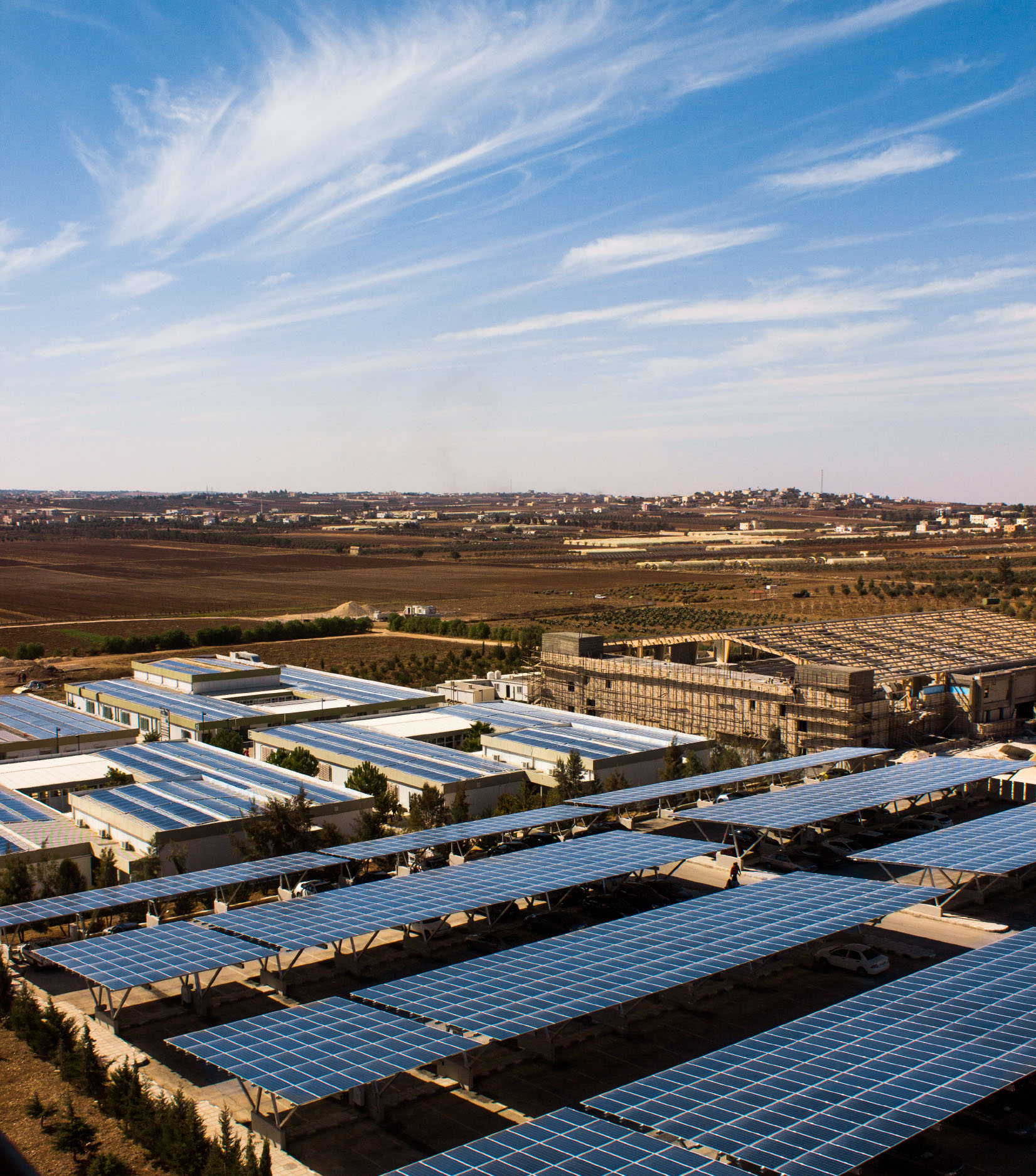
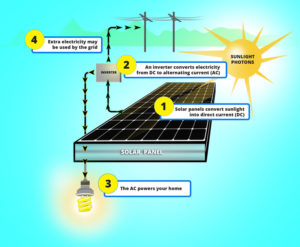
The sun is a natural nuclear reactor that releases small packets of energy called photons. These photons travel the long distance from the sun to Earth, approximately 93 million miles, in 8.5 minutes. Enough photons reach our planet on an hourly basis that will allow us to generate solar energy that will last the entire earth for a year. Although solar energy currently accounts for only about 19 percent of the planet’s energy consumption, it is currently on the rise and has become the world’s fastest growing source of power.
Solar panels, what we use to generate solar energy, are made up of solar cells. These solar cells are made of silicon, like semiconductors. Each solar cell has a negative layer and a positive layer with conductors attached to each layer. Once photons from the sun reach the solar cells, they knock the electrons loose from the cells’ atoms, forming an electrical circuit. When electrons flow through the electrical circuit, electricity is generated.